According to the relevant laws and regulations of mainland China, you can only use social acceleration after passing real-name authentication.
According to the relevant laws and regulations of mainland China, you can only use social acceleration after passing real-name authentication.According
to the relevant laws and regulations of mainland China, you can only use social acceleration after passing real-name authentication.

[Easy to Understand] Nodes, Routes & Protocols: How Is Your Data Accelerated?
#Tutorials & Guides
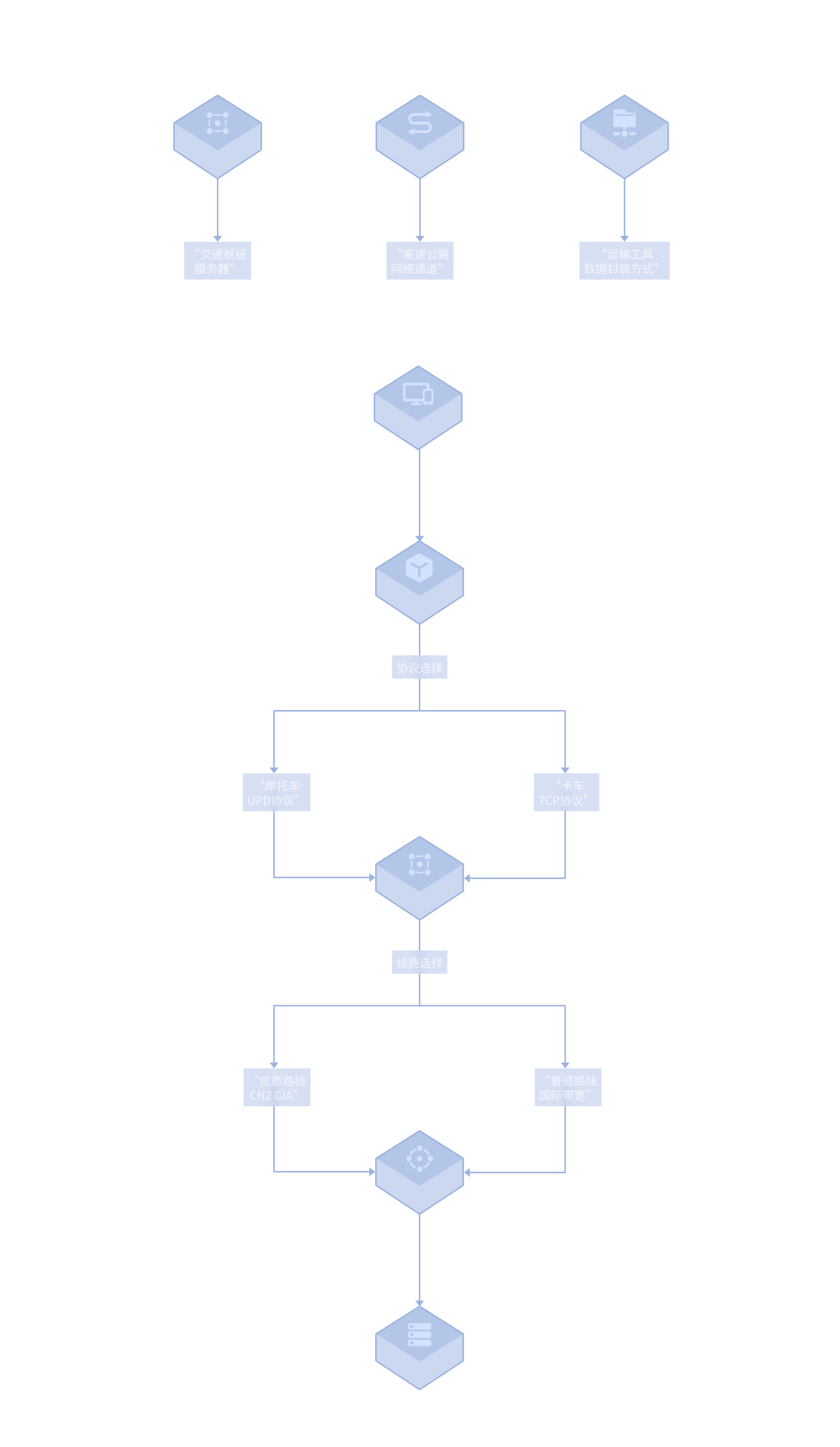
To make an analogy: Your network data is like a car, and the accelerator is like an "intelligent traffic system."
What Are Nodes?
1. Nodes are servers distributed worldwide, equivalent to "traffic hubs" or "transfer stations."
2. When you connect to the accelerator, your data no longer goes directly to the destination (such as game servers), but first goes to the nearest, uncongested "hub"
(node), then this hub uses the optimal highway to reach the destination directly.
3. The benefit of "massive nodes" is that you can always find a hub that's close to you and not congested, avoiding detours and traffic jams.
What Are Routes?
Routes are "dedicated highways" connecting these hubs. They determine the path your data takes from point A to point B. High-quality routes (such as CN2 GIA, BGP
routes) are like super highways with smooth surfaces, no toll booths, and green lights all the way, going directly from "local hub" to "target hub" with fast speed and
no detours.
What Are Protocols?
Protocols can be understood as "rules and packaging methods" for data transportation.
For example, some protocols (like UDP) are like "motorcycles" - fast and flexible, suitable for games with high real-time requirements, but may occasionally drop
packets.
Some protocols (like TCP) are like "container trucks" - reliable and stable, ensuring data arrives without loss, suitable for web browsing and file transfer, but may be
slightly slower.
Our "intelligent multi-channel" technology automatically selects the most suitable "vehicle" for the current network environment.
Our "intelligent multi-channel" technology automatically assigns you the appropriate vehicle (protocol) and navigates to the optimal hub (node) and the smoothest
dedicated highway (route), achieving an ultra-fast experience throughout the journey.
We hope these simple explanations help you better understand how accelerators work!


 service@speedx.link
service@speedx.link